Thermoforming plastic, a manufacturing process that involves heating and shaping thermoplastic sheets or films into desired forms, has revolutionized how businesses across industries approach product design and development. This versatile technique allows for the creating intricate, complex shapes and structures, catering to various applications, from packaging and automotive components to medical devices and consumer goods.
In a world where innovation and creativity are paramount, thermoforming plastic emerges as a game-changer, shattering the limitations imposed by traditional manufacturing methods. This innovative process empowers designers and engineers to push the boundaries of what’s possible, unleashing unprecedented design possibilities.
Limitations of Traditional Manufacturing Methods
Conventional manufacturing processes, such as injection molding and machining, have long been the industry standards, but they come with inherent constraints. Injection molding, while efficient for mass production, restricts designers to relatively simple geometries and shapes due to the complexity of mold designs. On the other hand, machining is often limited by the properties of the raw materials and the capabilities of the cutting tools.
These traditional methods often need help to accommodate intricate details, complex curves,
and unique designs, hindering the realization of truly innovative products. Designers are forced to compromise their visions, sacrificing form or function to comply with the limitations of the manufacturing process.
Furthermore, traditional manufacturing can restrict material choices, limiting the range of textures, colors, and finishes for product development. This lack of versatility can hinder differentiation and customization, crucial factors in today’s competitive market.
The Thermoforming Advantage

1.Versatility:
One key advantage of thermoforming plastic is its ability to create complex geometries and intricate details precisely. The process allows for the formation of deep draws, sharp corners, and intricate undercuts, producing truly unique and visually striking products.
This design versatility opens up endless possibilities for product differentiation and customization. Businesses can now offer tailored solutions to meet their customers’ specific needs, setting themselves apart from competitors and creating a unique brand identity.
2.Material Flexibility:
Thermoforming accommodates a wide range of thermoplastic materials, including polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polystyrene (PS), polypropylene (PP), and various types of polyethylene. This material flexibility ensures that designers and engineers can select the most suitable material for their application, considering strength, durability, transparency, and chemical resistance.
Additionally, thermoforming allows for incorporating different textures, colors, and finishes into the final product. This capability enables the creation of visually stunning and tactile designs, enhancing the overall user experience and product appeal.
Shattering Design Limitations with Thermoforming
Thermoforming has created innovative and eye-catching packaging designs for various industries, including food, cosmetics, and electronics. The ability to form intricate shapes and incorporate branding elements directly into the packaging has revolutionized product presentation and shelf appeal.
The automotive industry has embraced thermoforming for producing interior and exterior components with intricate designs, such as dashboard panels, door trim, and spoilers. These components often feature complex curves, undercuts, and textured surfaces, which would require more than traditional manufacturing methods.
In the medical field, thermoforming has enabled the creation of devices with precise, intricate designs that enhance functionality and user experience. Examples include surgical instrument trays, prosthetic components, and custom orthotics, all of which require complex geometries and attention to detail.
Thermoforming facilitates rapid prototyping, allowing designers and engineers to visualize and refine their concepts quickly. This iterative process enables them to make adjustments and improvements, leading to faster product development cycles and reduced time-to-market.
Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that often require significant upfront investments in tooling and molds, thermoforming is well-suited for producing one-of-a-kind products or small production runs. This flexibility is particularly valuable for businesses operating in niche markets or those seeking to test new product ideas before committing to large-scale production.
Overcoming Challenges in Thermoforming
While thermoforming plastic offers numerous advantages, it is essential to acknowledge the importance of expertise and experience. Skilled thermoforming professionals can navigate the complexities of material selection, mold design, and process parameters to ensure consistent quality and optimal results.
The right thermoplastic material and processing parameters are crucial for achieving the desired product characteristics. Factors such as material thickness, temperature, vacuum pressure, and cooling rates must be carefully controlled to prevent defects like warping, shrinkage, or surface imperfections.
Another key challenge in thermoforming is achieving consistent quality and accuracy. Variations in material properties, environmental conditions, or equipment settings can impact the final product dimensions and tolerances. Rigorous quality control measures, combined with advanced monitoring and adjustment systems, are essential to maintaining the desired level of precision.
The Economic Benefits of Thermoforming
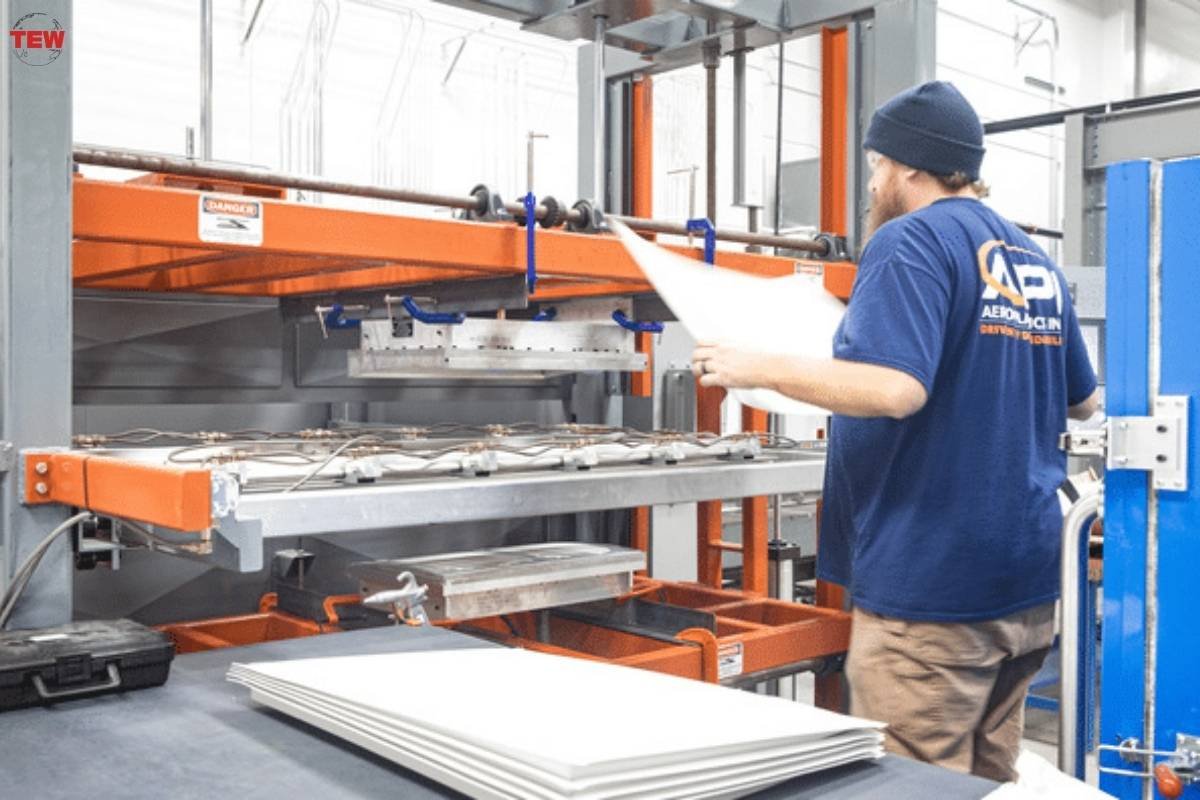

In addition to its design advantages, thermoforming plastic offers economic benefits that make it an attractive choice for businesses across various industries. One key advantage is its cost-effectiveness for low to medium production volumes, particularly when compared to processes like injection molding, which often require substantial upfront investments in tooling and molds.
Thermoforming typically requires less complex and less expensive tooling than other manufacturing methods, making it a more accessible option for businesses with limited budgets or those seeking to minimize initial investment costs.
Moreover, thermoforming offers the potential for cost savings through material optimization and waste reduction. By carefully designing and nesting molds, businesses can maximize material utilization and minimize scrap, reducing overall material costs and reducing environmental impact.
Thermoforming and Sustainability
In an era where sustainability and environmental responsibility are paramount, thermoforming plastic presents an opportunity to create eco-friendly products while minimizing resource consumption and waste.
One key advantage of thermoforming is utilizing recycled and recyclable thermoplastic materials, reducing the reliance on virgin plastics and contributing to a circular economy. Many thermoformed products can be easily recycled at the end of their life cycle, further reducing their environmental impact.
Additionally, modern thermoforming processes are designed to be energy-efficient, minimizing the overall carbon footprint associated with production. Businesses can reduce their energy consumption and related greenhouse gas emissions by optimizing heating and cooling cycles and implementing energy-saving technologies.
The Future of Thermoforming Plastic

As technology continues to evolve, the thermoforming industry is poised to embrace new trends and advancements that will further expand its capabilities and applications. Innovations in materials science, mold design, and process automation are expected to drive the evolution of thermoforming, unlocking new possibilities for product design and manufacturing.
One of the most promising areas for thermoforming’s expansion is the exploration of new industries and markets. From aerospace and transportation to architecture and construction, thermoforming plastic’s versatility and design freedom make it an attractive solution for various applications, each with its unique requirements and challenges.
Furthermore, thermoforming is well-positioned to play a crucial role in sustainable and eco-friendly product design. As consumer demand for environmentally conscious products grows, businesses can leverage thermoforming’s ability to incorporate recycled materials and minimize waste, creating sustainable solutions that meet functional and ethical standards.
Conclusion
Thermoforming plastic has revolutionized product design by shattering limitations. This versatile process allows the creation of complex shapes and intricate details, empowering businesses and designers to unlock new levels of creativity. With its ability to handle various materials, textures, and finishes, thermoforming helps companies differentiate their products and cater to ever-changing consumer demands.