About 40 million medical procedures are conducted with the help of sedation annually in the USA. Sedation refers to the use of medications to induce a relaxed state. There are different levels, from minimal sedation (you can still respond to verbal commands) to general anesthesia (you are unconscious and pain-free). Sedation allows patients to undergo medical procedures they might otherwise find unpleasant or painful.
To address some popular misconceptions, check the 7 most asked questions people ask about sedation.
1. How Does Sedation Administration Differ for Pediatric Patients Compared to Adults?
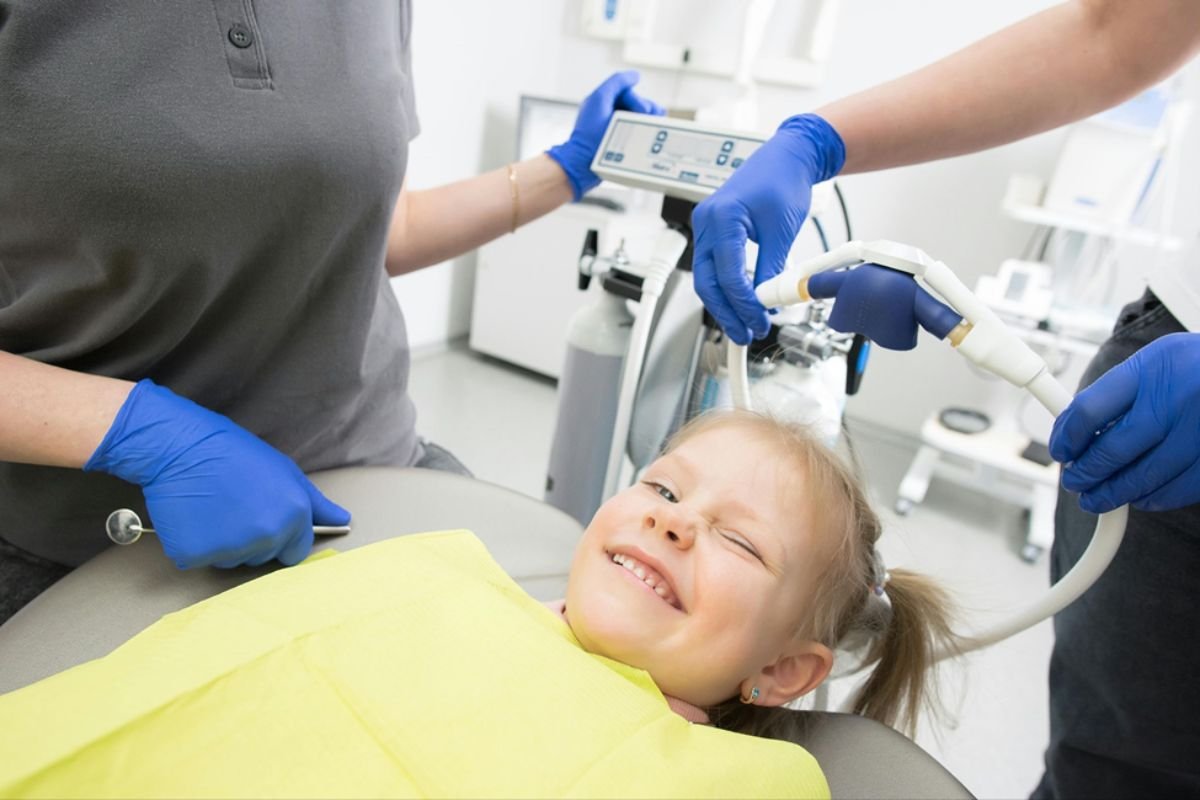
When providing sedation to pediatric patients, extra care and precautions must be taken. Their developing bodies metabolize drugs differently. Pediatric patients also can’t communicate problems as clearly as adult patients. Providers who completed safe sedation training understand these differences.
The dosing is calculated based on the child’s weight and is administered incrementally to avoid oversedation. Children are at higher risk of airway obstruction and breathing issues during sedation, so pediatric sedation providers are specially trained in airway management and monitoring breathing and oxygen levels. The medications used may also differ to minimize risks in children.
2. Can Sedation Be Combined With Pain Management?
Yes, an analgesic (pain relief medication) is often combined with sedation for procedures. The sedative helps the patient relax and duringthe procedure, while the analgesic blocks the pain. Combining the two medications, allows doctors to perform procedures with maximum patient comfort.
The types and amounts of medications are tailored to the patient and procedure. The procedure may be performed in a hospital, outpatient surgery center, doctor’s office, or dentist’s office.
3. How Is the Risk of Allergic Reactions to Sedative Medications Managed?
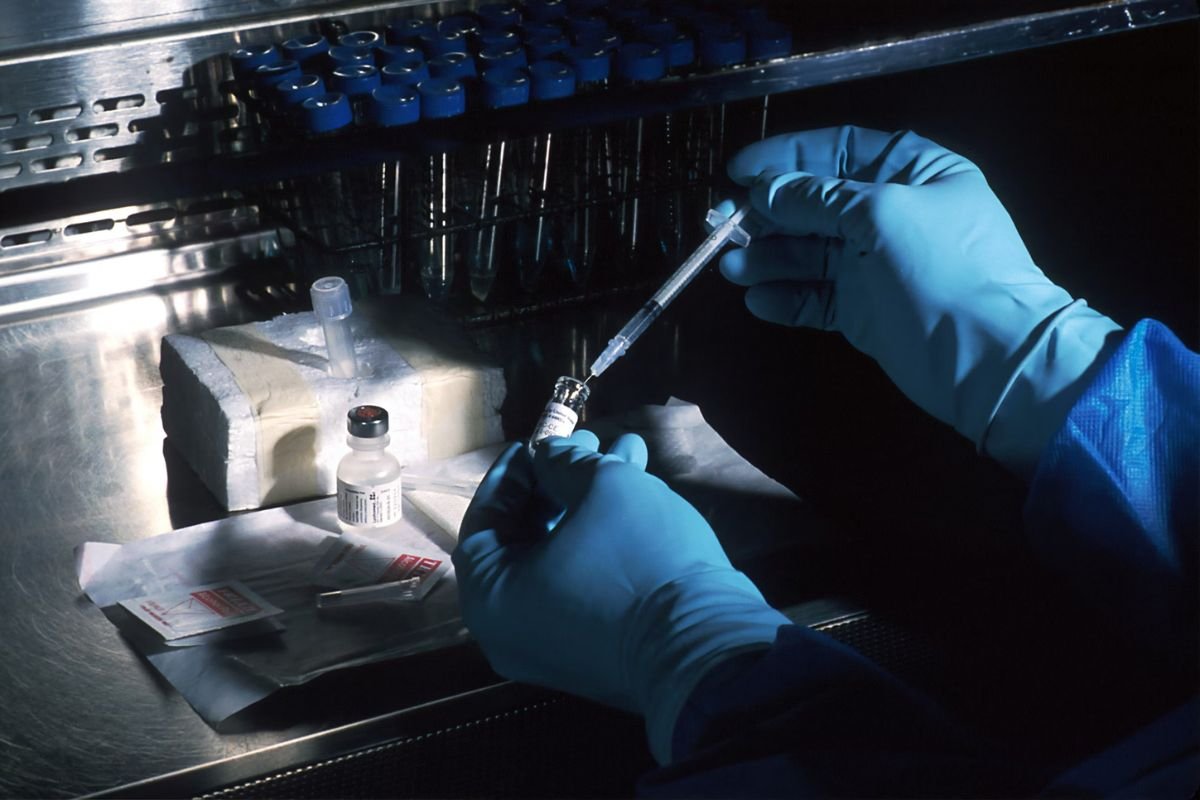
Before sedation, patients are asked about medication allergies and sensitivities. They can also be screened for medication allergies and risk factors. If a patient reports an allergy, alternative medications are chosen.
Providers perform allergy skin testing for high-risk medications like penicillin. For sedation, they choose alternative agents less likely to cause reactions.
Resuscitation equipment and emergency medications are on hand in case of anaphylaxis. Vital signs are closely monitored for any signs of an allergic response during and after sedation. Using the lowest effective dose also minimizes allergic response. With proper precautions and a trained care team, the risk of allergic reactions can be minimized for safe sedation.
4. What Advancements in Sedation Technology are Currently Being Researched?
The global market for dental sedation was valued at over $1.9 billion in 2023, with projected growth to $2.8 billion by 2030. The field of sedation is constantly evolving, with new advancements improving both safety and effectiveness.
- Integration with digital monitoring tools. Advancements in monitoring technology enable improved management of sedation levels, thereby enhancing patient safety.
- Development of targeted sedatives. New formulations have been developed to offer effective sedation with minimal side effects.
- Improved recovery protocols. Improvements in recovery processes ensure faster patient recovery after sedation, enhancing overall effectiveness.
- Customizable sedation protocols. Tailored protocols can be adjusted to meet individual patient needs and procedural requirements.
Continuous improvements in educational programs will ensure that medical professionals stay up-to-date with the latest sedation techniques.
5. How Does Sedation Impact Memory and Awareness?
One common concern among individuals considering sedation is its potential impact on memory and awareness. Sedation affects your central nervous system to induce a relaxed, sleepy state. The level of sedation is carefully controlled. The sedatives used typically do not eliminate your memory of the procedure or your awareness of your surroundings.
With light sedation, you’ll feel relaxed but still conscious and able to respond. Moderate sedation impairs memory and awareness to some extent. Under deep sedation, you’ll be in a sleep-like state without memory of the procedure.
6. What Are the Considerations for Sedation in Elderly Patients?
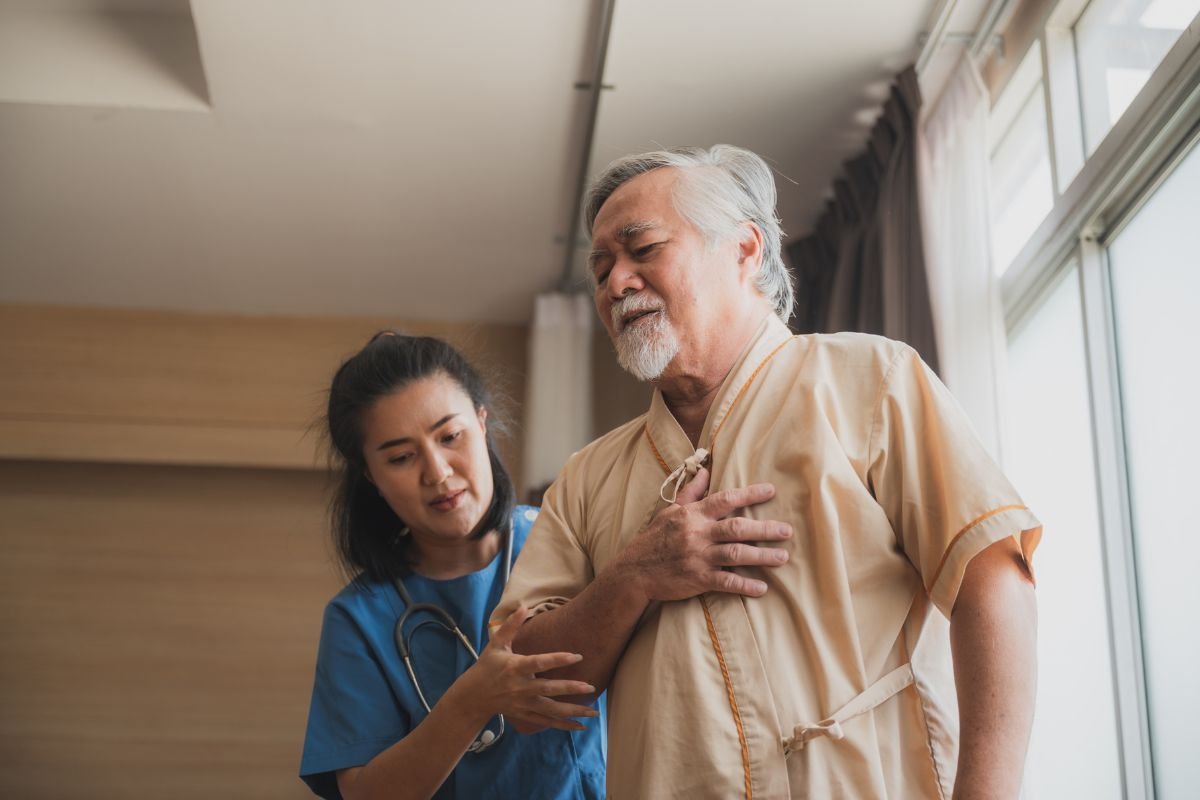

Sedating elderly patients requires extra caution due to age-related changes in metabolism and body composition. They often need lower medication doses.
With age, the body becomes more sensitive to sedatives and processes them more slowly. Medical professionals carefully adjust doses to prevent overly deep sedation in elderly patients. They also monitor vitals to ensure safety.
Pre-sedation medical exams help identify underlying conditions needing special precautions. Sedation is safe for seniors when administered by professionals trained in geriatric care.
7. How Do Dentists Determine the Appropriate Level of Sedation for a Patient?
The level of sedation depends on factors like the medication used and your response. Lighter levels allow you to follow instructions during procedures. Deeper sedation causes amnesia but is still safe with proper monitoring.
The best sedation level depends on the procedure and your needs. For minor procedures, light sedation reduces anxiety while allowing you to stay awake. For more invasive treatments, moderate or deep sedation prevents discomfort and memory formation.
Dentists consider factors like your patient’s medical history, anxiety levels, and individual tolerance to sedatives when deciding on sedation depth. Don’t hesitate to discuss all your questions and concerns with your dentist.
Conclusion
Sedation technology is always improving. It minimizes anxiety and makes procedures as easy as possible. With the proper safeguards and highly-trained specialists, sedation can be administered safely to adult and pediatric patients. However, patients should always discuss concerns with their doctor before a procedure requiring sedation.






